
Have you ever felt pain in your elbow after an activity, whether it's sports, work, or simply repetitive movements? It could be golfer's elbow or tennis elbow. Both cause pain around the elbow, but they have different pain locations, causes, and risk factors.
Although its name is associated with certain sports, this condition affects not only golfers and tennis players, but also anyone who frequently uses their arms and wrists repetitively. Recognizing the difference between golfer's elbow and tennis elbow is crucial for more appropriate and effective treatment.
Get to Know Golfers Elbow: An Injury to the Inside of the Elbow
Golfer's elbow, or medial epicondylitis in medical terms, is an injury or inflammation of the tendons attached to the inside of the elbow. These tendons connect the forearm muscles to the bones and play a crucial role in gripping, wrist bending, and arm rotation. Golfer's elbow isn't unique to golfers; it can affect anyone who repeatedly uses their forearm muscles.
Common Causes and Symptoms of Golfer's Elbow
The main cause of golfer's elbow is repetitive wrist flexion movements, for example when playing golf, lifting weights, throwing a ball, continuous typing, or manual work that involves a lot of hand movement.
Symptoms usually include:
- Pain or a burning sensation on the inside of the elbow, which may radiate to the forearm.
- Stiffness in the elbow.
- Weakness when gripping or lifting objects.
- Sometimes accompanied by a tingling or numb feeling in certain fingers.
Getting to Know Tennis Elbow Better
Tennis elbow, or lateral epicondylitis in medical terms, is an injury or inflammation of the tendon attached to the outside of the elbow. This tendon helps straighten the wrist and fingers.
Symptoms and Causes of Tennis Elbow
The main cause of tennis elbow is repetitive wrist extension movements, for example when playing tennis or other racket sports, typing, using a screwdriver, or work that involves twisting movements of the arm and wrist.
Symptoms usually include:
- Pain or soreness on the outside of the elbow, which may radiate to the forearm.
- Pain when gripping or lifting objects, even light ones.
- Weakness in the wrist.
- Pain that worsens when lifting, turning, or shaking another person's hand.
Just like golfer's elbow, this condition is not only experienced by tennis players, but also anyone who frequently uses their forearms in repetitive motions.
Key Differences Between Golfers Elbow and Tennis Elbow
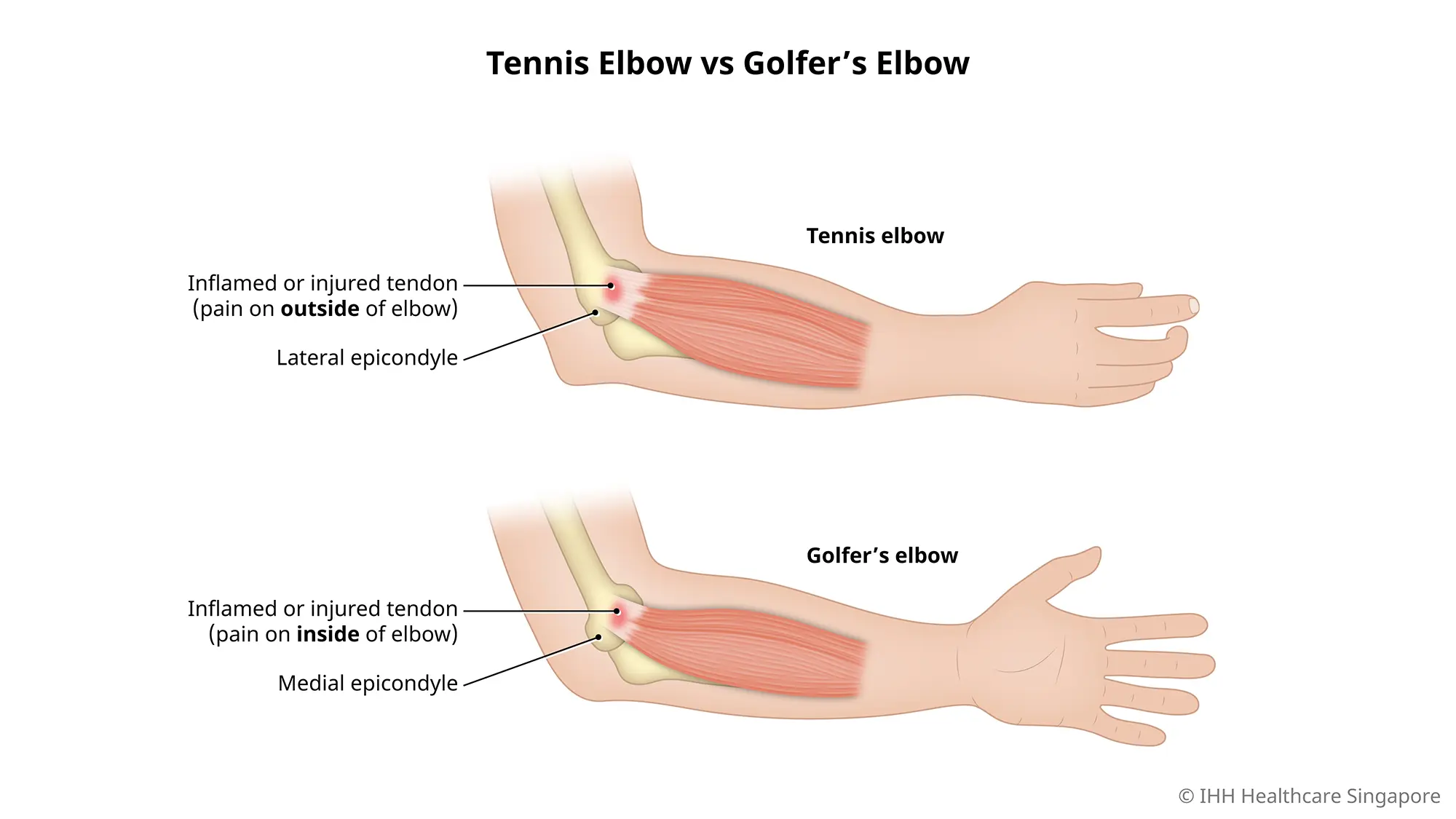
Although both cause pain in the elbow area, golfer's elbow and tennis elbow have quite distinct differences. Here are the most easily identifiable key differences between golfer's elbow and tennis elbow:
1. Location of pain
Golfers Elbow: the inside of the elbow
Tennis Elbow: the outside of the elbow
2. Type of movement that triggers
Golfers Elbow: a downward bending motion of the wrist (flexion)
Tennis Elbow: a movement that straightens or pulls the wrist upwards (extension)
3. Trigger activity
Golfers Elbow: golf, weight lifting, throwing a ball, typing, repetitive manual work
Tennis Elbow: tennis, racquet sports, typing, using a screwdriver, work involving twisting movements
4. Typical symptoms
Golfers Elbow: pain radiates to the inside of the forearm, grip feels weak
Tennis Elbow: pain radiating to the outer side of the forearm, difficulty lifting light objects
Tips to Prevent Golfer's Elbow and Tennis Elbow
Now that we understand the differences and risk factors between tennis elbow and golfer's elbow, it's important to know how to prevent them. With the right preventive measures, the risk of elbow pain can be minimized while still carrying out daily activities. Here are some ways to do this:
- Warm up before exercise or strenuous activity.
- Use the correct technique when exercising or working.
- Set up an ergonomic working position , especially if you often type or use a mouse.
- Give your hands a rest if they have been used for a long time for repetitive movements.
- Regular stretching and strengthening exercises for the forearm muscles .
When Does Elbow Pain Require Medical Treatment?
Not all elbow pain requires medical treatment, as most can improve with rest and self-care. However, you should consult a doctor immediately if the pain persists after a few weeks, worsens to the point of interfering with daily activities, or is accompanied by other symptoms such as swelling, redness, tingling, or muscle weakness in the arm. With a proper medical examination, your doctor can determine the cause of the pain and prescribe appropriate treatment to prevent further worsening.
Article written by Dr. Marco Ariono Nainggolan, Sp.KO (Sports Medicine Specialist, EMC Pekayon Hospital).
