
Is a clinical condition where there is a non-traumatic blood circulation disorder that occurs acutely in a focal area of the brain resulting in focal and global neurological function disorders.
Clinical symptoms: numbness, weakness to paralysis of the limbs, headache, slurred speech, loss of balance and blurred vision.
Cause:
- Bleeding Stroke (Hemorrhagic CVD)
- Ischemic Stroke / Blockage (Non Haemorrhagic CVD)
An overview of the difference between Ischemic Stroke & Hemorrhagic Stroke.
Epidemiological studies show that stroke is the main cause of chronic disability and one of the highest causes of death. Increases according to age and the sex ratio is slightly dominated by pnia compared to women. Incidence: Bleeding Stroke 25% & Ischemic Stroke 75%.
Risk factors include:
- Hypertension
- Smoke
- Blood lipid levels
- Alcohol
- Antiplatelet therapy
- Hereditary
- stress
Ischemic Stroke / Blockage (Non Hemorrhagic)
Dominated by the middle age and older adult groups, most of which are closely related to the incidence of atherosclerosis (thrombosis) and heart disease (embolism). Occlusion or occlusion of the cerebral vessels can be caused by an embolism, an antegrad thrombus or intrinsic disease of the cerebral vessels themselves.
Atherosclerosis in the form of a plaque accumulation of endothelium, intima cells, smooth muscle cells and lipids (cholesterol and cholesterol esters).
This plaque will cause narrowing of the arterial lumen or even can completely block it due to stagnant blood clots in that location, eventually causing an infarction at the distal end.
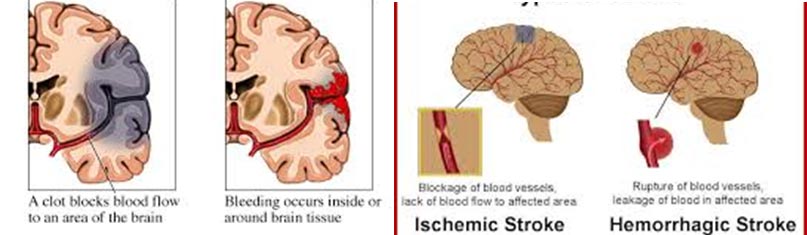
Picture of blockage/narrowing of brain blood vessels & CT scan.
The goal of therapy:
- Establish a diagnosis of cerebral ischemia and its etiology as soon as possible.
- Recognizing that there is a period of time when ischemia is still reversible, plan a strategy of investigation and treatment based on that.
- Giving specific therapy according to the pathogenesis of ischemia.
- Look for and treat other conditions that exacerbate ischemia
Bleeding (Hemorrhagic) Stroke
Includes intracerebral / intraparenchymal bleeding: 75%
Subarachnoid hemorrhage 25%.
Causes of bleeding: hypertension, cerebrovascular disease: AVMs, aneurysm, sinus thrombosis, consumption of anti-coagulant drugs, hemorrhagic disorders, cerebral hemorrhagic infarction, bleeding brain tumors. Has a death rate or mortality reaches 80%.
Indications for a CT scan / MRI:
- Decreased consciousness.
- Persistent neurological deficit.
- Persistent disturbance of consciousness.
- Complaints of persistent headache.
- There is a seizure attack.
- Stiff neck
Location of bleeding:
- Putamen and Internal Capsule
- thalamus
- Alba substance
- cerebral hemisphere
- Punch
Therapy includes operative and non-operative.
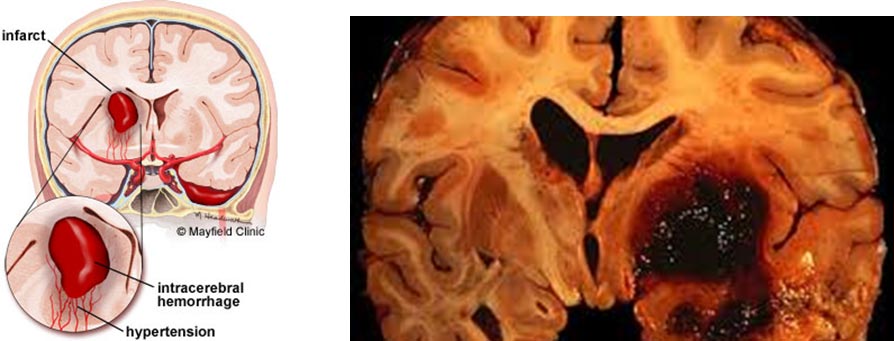
Location of Bleeding Stroke due to hypertension.
Article written by a Neurosurgeon Specialist at EMC Sentul Hospital.
